Eli Lilly Partners with Creyon Bio in up to $1B AI-Oligonucleotide Deal
Eli Lilly has signed a strategic partnership with Creyon Bio to develop AI-designed oligonucleotide therapeutics, committing $13 million upfront and up to $1 billion in performance-based milestone payments. The deal grants Lilly exclusive rights to lead candidates from Creyon’s platform, which applies machine learning to engineer RNA- and DNA-based molecules for modulating gene expression.
Creyon Bio, launched in 2022 with $40 million in Series A funding and staffed by executives from Ionis Pharmaceuticals, has built what it terms an "AI-Powered Oligo Engineering Engine". This platform applies data-driven models to design RNA- and DNA-based drugs capable of modulating gene expression through various mechanisms such as knockdown, splice-switching, or upregulation—bypassing traditional trial-and-error approaches.
As part of the new deal, Lilly receives an exclusive license to pursue select programs generated by Creyon. No details were disclosed about the specific disease areas or the number of targets involved. Outside of the Lilly collaboration, Creyon continues to develop its internal pipeline, with its lead neuromuscular disease candidate expected to enter clinical trials next year.
This marks Lilly’s second AI-oligonucleotide collaboration in less than a year. In 2024, it signed a $409 million total potential value deal with Genetic Leap, and earlier, a $45 million upfront partnership with QurAlis for a splice-switching antisense candidate.
Creyon Bio’s Oligonucleotide Design Approach
Creyon Bio develops oligonucleotide-based medicines (OBMs) using a platform that combines biophysics, genomics, and machine learning to model how chemical and structural features impact pharmacological outcomes. Rather than relying on trial-and-error screening, the system uses large, curated datasets to train predictive models that estimate the safety, efficacy, and mechanism of action for candidate sequences.
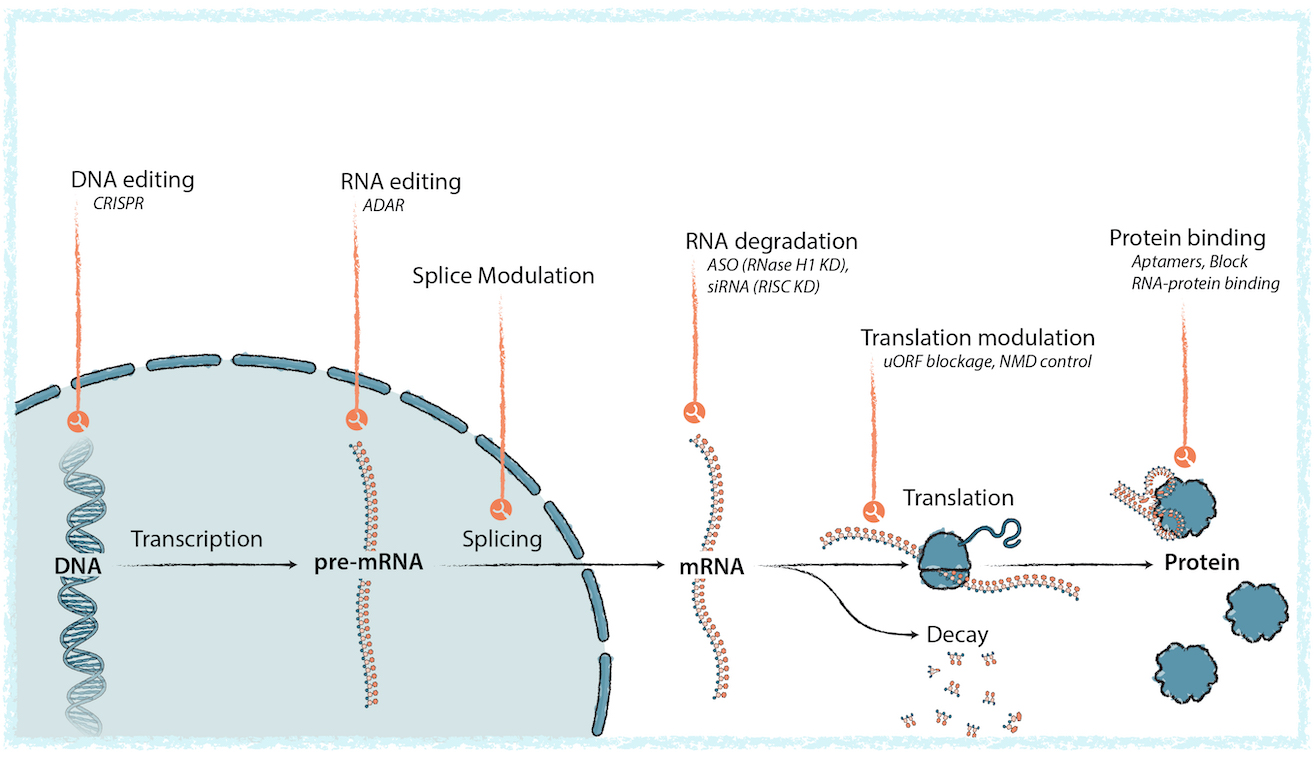
Modular sites of therapeutic intervention with oligonucleotide-based medicines (OBMs), targeting gene expression from DNA transcription through RNA processing to protein interaction. Credit: Creyon Bio.
OBMs such as antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), siRNA, and RNA-targeting aptamers operate through base-pairing interactions with target transcripts. Creyon’s platform captures how variations in sequence, backbone chemistry, and sugar modifications affect performance metrics like tissue specificity, half-life, and off-target effects. Given the design space—billions of possible combinations for short sequences—the platform focuses exploration on regions with higher predicted utility, allowing for more efficient candidate selection and early risk assessment.
The models are used both for internal pipeline development and partner-driven discovery programs.
Topics: AI & Digital