Roivant Spinout Debuts AI Model to Combine Biomolecule Structure Prediction and Generation
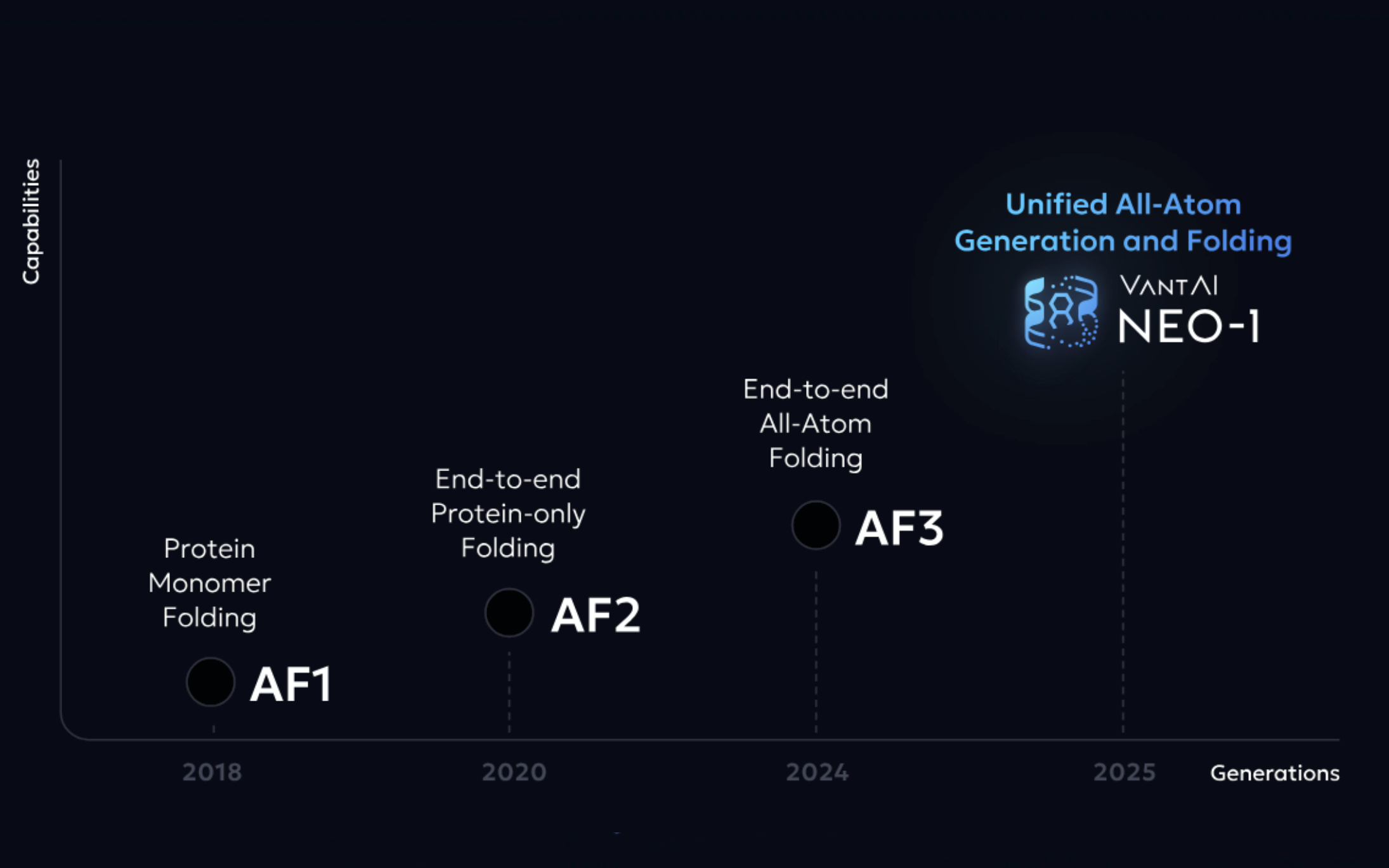
VantAI, a NY-based spinout of Roivant founded in 2019, has introduced Neo-1, an artificial intelligence model that integrates atomic-level biomolecule structure prediction with molecular generation in a single framework.
Neo-1 was unveiled at NVIDIA’s GTC 2025 conference. VantAI’s CTO Luca Naef told Endpoints News that Neo-1 “tackles the big next step after AlphaFold 3”—a model developed by Google DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs—by integrating biomolecule structure prediction with the design of new molecules to address a critical bottleneck in drug discovery.
The model generates latent representations of entire molecules, which can be decoded into atomic-level structures. This process enables it to simultaneously predict protein–small molecule interactions and generate novel compounds. Its multimodal capabilities allow Neo-1 to work with complete or partial structural and sequence inputs, as well as experimental data, to model complex protein–ligand interactions.
Neo-1 reported capabilities in comparison to AlphaFold foundation models. Source: Vant.ai
It is designed to improve drug discovery efficiency by narrowing the search space for viable candidates and enhancing the precision of molecular design. According to Michael Bronstein, Chief Scientist at VantAI and DeepMind Professor of AI at the University of Oxford, the model decodes the “geometric vocabulary of protein interaction at the full proteome scale.”
Neo-1’s development involved large-scale training on structural and synthetic datasets using hundreds of NVIDIA H100 GPUs. The model integrates VantAI’s proprietary dataset titled “NeoLink,” which captures structural data using cross-linking mass spectrometry (XLMS). As stated in the whitepaper, "...with NeoLink, structural data can be obtained for the whole cell at once, exceeding the throughput of current structure measurement paradigms by several orders of magnitude at a fraction of their cost."
Optimized in collaboration with NVIDIA, Neo-1 incorporates custom datasets and synthetic data generated using GPU-mmseqs2, a tool co-developed with NVIDIA and SNU, and leverages NVIDIA’s recently announced MSA-Search NIM to boost structure prediction efficiency.
Naef said that Neo-1 enables de novo generation of complex drug-like molecules, including molecular glues and bifunctional degraders—mechanisms that have been difficult to target using conventional methods. Its ability to co-fold and design new molecules simultaneously could allow it to target previously undruggable proteins.
Neo-1 is already in use across three major pharmaceutical and biotech partnerships, including collaborations with Janssen (J&J), Blueprint Medicines, and Bristol Myers Squibb. VantAI expects the model to accelerate its internal drug discovery pipeline, and there’s an ongoing collaboration with Boehringer Ingelheim since 2022 focused on novel protein degraders.
VantAI’s scientific advisory board includes Fan Liu, professor of structural interactomics at Charité and FMP; Philippe Schwaller, head of the Laboratory of Artificial Chemical Intelligence (LIAC) at EPFL; Bruno Correia, associate professor and leader of the Laboratory of Protein Design & Immunoengineering at EPFL; Ian Churcher, former CSO at Amphista and SVP of drug development at Benevolent; and Bradley L. Pentelute, professor of chemistry at MIT and associate member of the Broad Institute.
Topics: AI & Digital