Vevo Therapeutics Open-Sources Largest Single-Cell Dataset with Arc Institute
Vevo Therapeutics has officially released the Tahoe-100M, described as the world’s largest single-cell dataset, in collaboration with the Arc Institute. The dataset, now open-source, serves as the inaugural contribution to the Arc Virtual Cell Atlas—a newly launched public resource that integrates single-cell transcriptomic data from over 300 million cells across various species, tissues, and experimental conditions.
The Arc Virtual Cell Atlas is now accessible via Arc’s portal. The Tahoe-100M preprint, which outlines the dataset’s structure and methodology, is available on bioRxiv.
Tahoe-100M comprises more than 100 million single-cell transcriptomic profiles, mapping how 1,100 small-molecule drug perturbations affect cells across 50 cancer cell lines. Developed using Vevo’s Mosaic platform, the dataset captures cellular responses across 60,000 experimental conditions—measuring drug-patient interactions at single-cell resolution. According to Vevo, Tahoe-100M is at least 50 times larger than all previously available drug-perturbed single-cell datasets combined.

Pre-print: "Diversity of cellular models and drug perturbations in Tahoe-100M. Mechanism of action grouping of the 379 drug perturbations in Tahoe-100M, further stratified by clinical trial status."
Enabling Predictive Models of Cellular Behavior
Tahoe-100M addresses a key challenge in cell biology: understanding how cells integrate multiple signals to produce specific transcriptional and phenotypic responses. Vevo indicates that the dataset systematically captures how cells react to a broad spectrum of perturbations, generating insights into gene function, signaling pathways, and potential feedback mechanisms.
A standout feature is its capacity to capture cellular heterogeneity—differences in gene expression and behavior occurring among genetically identical cells. Although bulk transcriptomic measurements often mask such variations, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) enables more granular resolution, and Tahoe-100M’s scale increases the likelihood of revealing subtle or rare patterns that population-level data might miss.
Mosaic Platform: Scaling Single-Cell Perturbation Studies
Vevo’s Mosaic platform played a central role in achieving the dataset’s scale and depth. It employs a “cell village” strategy, pooling diverse cancer cell lines in a shared environment for parallel testing. Vevo reports that this configuration minimizes batch effects and facilitates high-throughput profiling across thousands of conditions.
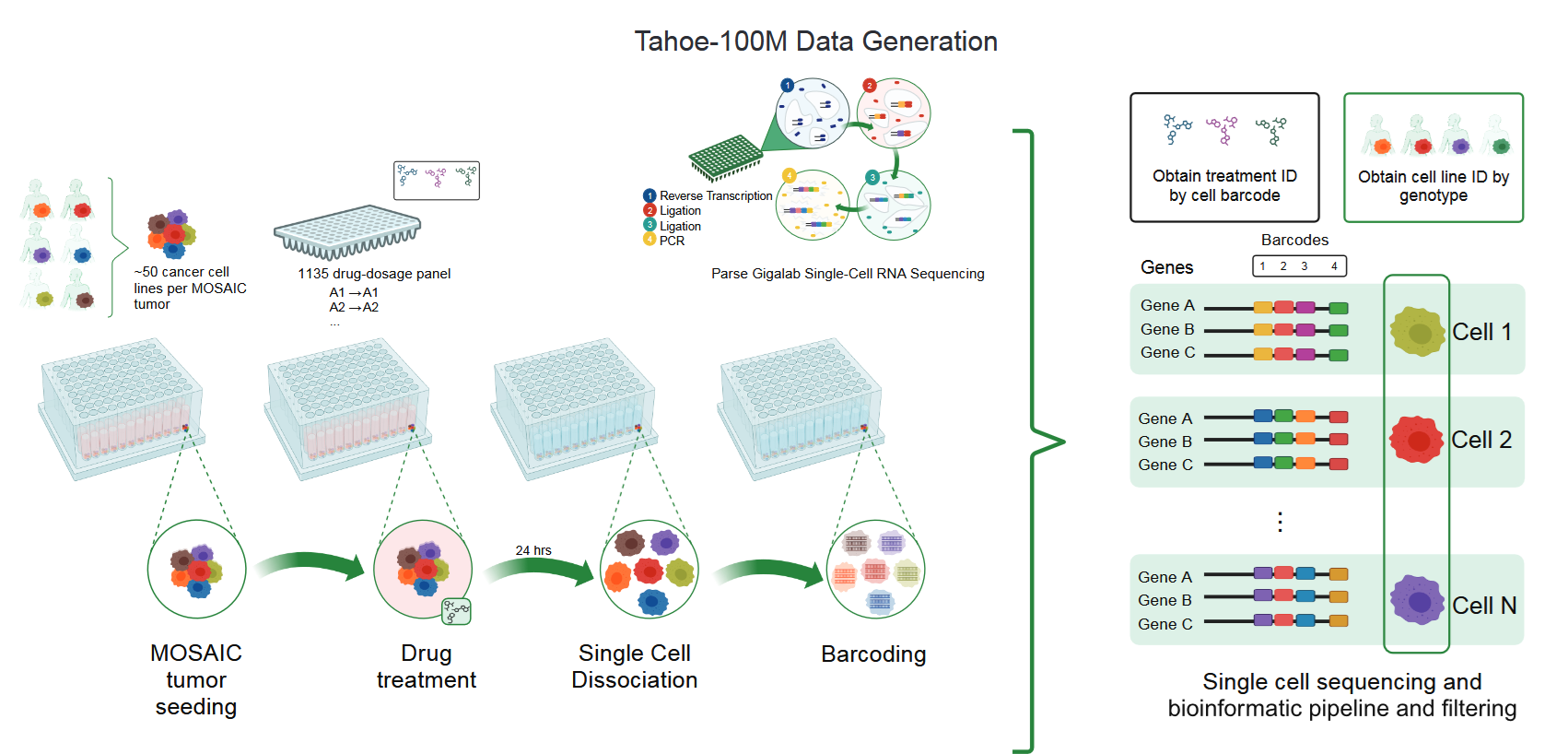
Pre-print: "Mosaic platform—experimental and informatics workflow used to generate Tahoe-100M. [...] Experimental schematic: each Mosaic tumor is composed of 50 cancer cell line models, seeded into 96-well plates. Each well receives a drug perturbation, and after 24 hours, tumors are dissociated into single cells and barcoded using the Parse GigaLab kit. These barcodes, along with the known genotypes of each cell line, enable treatment and cell line deconvolution."
Vevo also reports that the Mosaic platform’s core design is flexible, extending beyond pharmacological research to accommodate genetic and environmental perturbations. Tahoe-100M is therefore positioned as a broadly applicable resource for investigating gene function and regulatory networks across various biological disciplines, not just oncology.
Integrating Observational and Perturbed Cell States for AI Modeling
The dataset now forms part of the Arc Virtual Cell Atlas, combining data from both natural (observational) and drug-perturbed cellular states. This also includes Arc’s scBaseCamp dataset, featuring 200 million single-cell transcriptomes across 21 species. The integrated resource enables researchers to compare how cells behave naturally versus under external interventions.
Dave Burke, Chief Technology Officer at Arc Institute:
"What makes the Arc Virtual Cell Atlas particularly powerful is not just its scale, but that now researchers can analyze together both observational natural cell states and cells that have been deliberately perturbed by drugs or chemicals to see how they respond.
Tahoe-100M was generated with support from Parse Biosciences’ GigaLab platform, which enabled large-scale single-cell sample preparation, and sequencing was conducted using technology from Ultima Genomics. This release builds on Vevo’s previous collaboration with Parse and NVIDIA, where Tahoe-100M was created in under a month using Parse’s Evercode split-pool barcoding system—enabling high-throughput sequencing without specialized equipment—and NVIDIA contributed AI model training and data engineering, advancing the integration of machine learning into drug discovery workflows.
Topics: AI & Digital