Recursion Unveils OpenPhenom-S/16: A Foundation Model for Microscopy Data
Recursion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (NASDAQ: RXRX) has released OpenPhenom-S/16, a new publicly accessible foundation model, on Google Cloud’s Vertex AI Model Garden. This development marks a meaningful step forward in how life sciences researchers leverage microscopy data for drug discovery and cellular analysis.
Advancing Microscopy Analysis
OpenPhenom-S/16 builds on Recursion’s earlier proprietary models, Phenom-1 and Phenom-2, which were developed for internal use and demonstrated significant advancements in Recursion’s drug discovery pipeline. These earlier models laid the groundwork for the publicly accessible OpenPhenom-S/16, incorporating insights gained from years of research and practical application.
See also: 19 Companies Pioneering AI Foundation Models in Pharma and Biotech
OpenPhenom-S/16 is a foundation model trained using self-supervised learning on over three million microscopy images from datasets like RxRx3 and JUMP-CP. The model aims to replace traditional microscopy analysis tools that require significant tuning and struggle with large-scale datasets. Recursion highlights the model’s ability to recall known biological relationships with accuracy outperforming legacy solutions, such as CellProfiler.
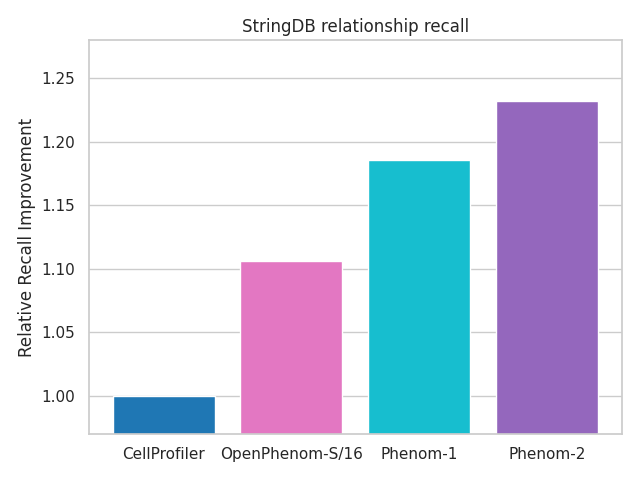
Figure 1. Here is how OpenPhenom-S/16 embeddings outperform traditional CellProfiler methods.
For instance, OpenPhenom-S/16 has demonstrated superior performance in identifying biological relationships within the JUMP-CP cpg0016 dataset, based on benchmarks such as the StringDB database (Figure 1; PLoS Comp Bio 2024). By embedding these capabilities into Google Cloud’s Vertex AI platform, OpenPhenom-S/16 can automate tasks like cellular structure classification and anomaly detection, enabling researchers to extract actionable insights from complex microscopy datasets.
The release of OpenPhenom-S/16 on Google Cloud’s Model Garden allows life sciences companies and researchers to integrate the model into scalable workflows. Shweta Maniar, Global Director of Life Science Strategy & Solutions at Google Cloud, noted that this collaboration could accelerate discoveries in biomedicine by simplifying the analysis of high-dimensional microscopy data.
Complementary Resources: RxRx3-Core Dataset
To support the adoption of OpenPhenom-S/16, Recursion has introduced the RxRx3-core dataset. This dataset provides labeled images of 735 genetic knockouts and 1,674 small-molecule perturbations, along with image embeddings generated by OpenPhenom-S/16. It is designed to enable researchers to probe concentration-response relationships and explore gene-drug associations to foster advancements in phenomics. According to Imran Haque, Ph.D., SVP of AI and Digital Sciences at Recursion, this dataset signifies a big step forward in mapping drug mechanisms of action.
Researchers can access OpenPhenom-S/16 through Google Cloud’s Vertex AI Model Garden or via Hugging Face. Additionally, the RxRx3-core dataset is available at RxRx.ai/rxrx3-core. For further updates on Recursion’s datasets and models, interested users can sign up at RxRx.ai.
Topics: Tools & Methods